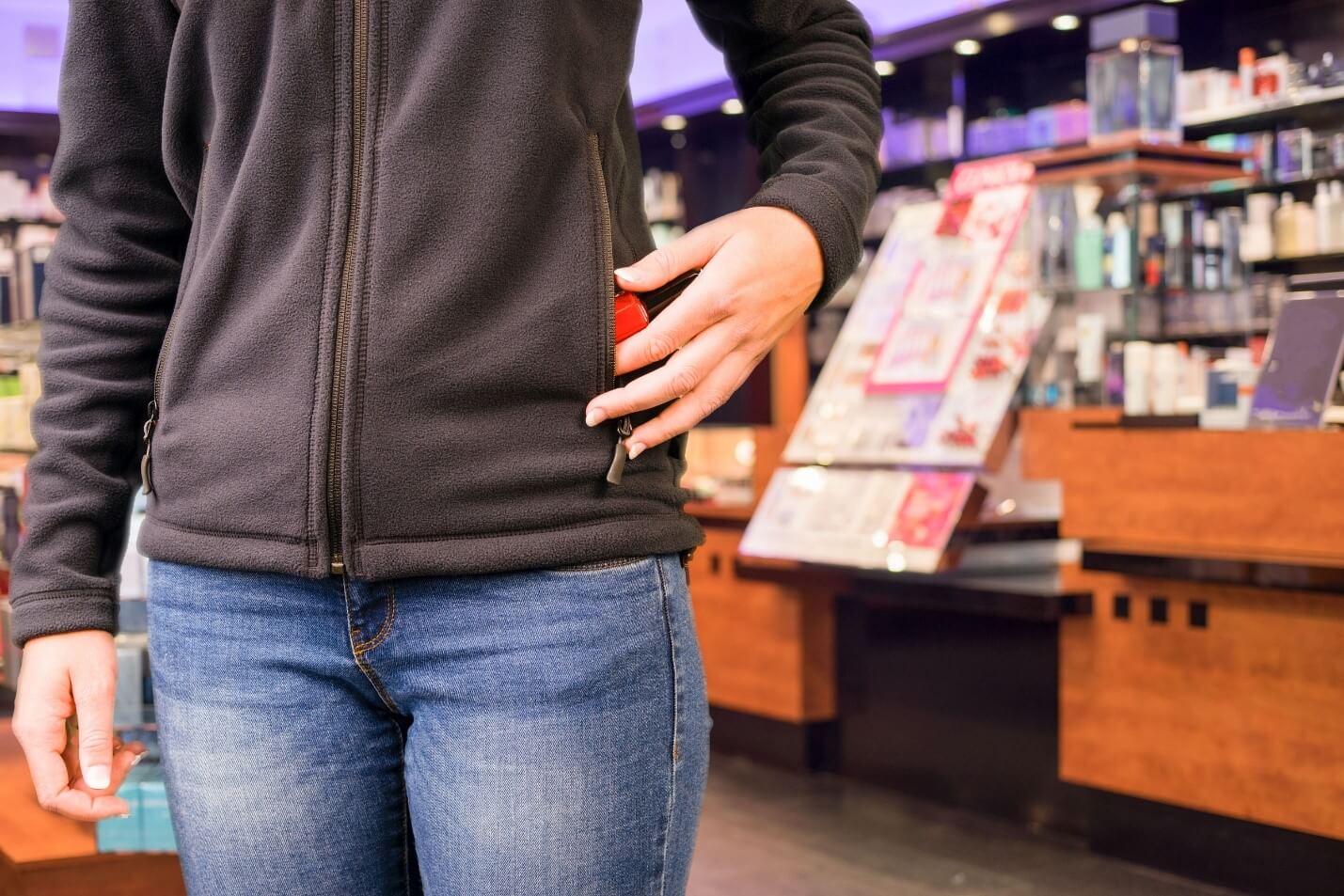
Definition of Nevada Petit Larceny
The intentional taking of another person’s property, without permission, can be called by many terms. For example, a charge of larceny may apply if a person actually steals or take away property. On the other hand, burglary would apply to entering a property with the intent to steal. It does not matter whether or not a theft actually occurred.
Nevada law uses the value of the items to define the severity of the offense. Petit larceny, also called shoplifting, petty larceny or petty theft, applies to stolen property of less than $650.00. It is a misdemeanor charge. Theft of property valued at $650.00 or over is considered grand larceny. This can carry a felony charge and much more serious consequences.
Petit larceny may be charged if a person intentionally steals; takes and carries away; leads, entices away or drives away personal goods or property owned by another person or entity.
Acts of petit larceny include:
- Shoplifting (also known as retail theft) – including concealment of merchandise, changing price tags, and switching products into different packaging for the purpose of theft.
- Hotel theft – including taking bedding, furniture, and other property intended for use in or with a person’s lodging.
- Theft of pets – including carrying or leading away; or enticing or driving away a domesticated animal or domesticated bird.
Penalties for Nevada Petit Larceny
NRS 205.240 states that in addition to any other penalty, the court shall order the person to pay restitution for a Nevada petit larceny. In other words, they will have to pay back the value of the stolen property. The value will be calculated at the highest value normal for that type of property.
A maximum sentence can include $1000 in fines and/or 6 months in jail. Additionally, an offender may have to complete a Petit Larceny course.
Other Considerations
A Nevada petty larceny may be a municipal crime in addition to a state crime. Nevada Attorney General Opinion 64 (June 16, 1959) states that a city may legally enact an ordinance making petit larceny a municipal offense if they are committed within the city, even though such acts are also offenses under state law; see, e.g., Reno Municipal Code § 8.10.040. – Petit larceny.
You may want to consider retaining a lawyer for a Nevada petit larceny charge. Common defenses include showing that the property belonged to the defendant, there was no intent to steal, and/or no property was actually taken. Additionally, a lawyer may be able to negotiate dismissal of charges. This typically would be in exchange for paying the fine, paying restitution and completing a petit larceny course. For a list of Nevada lawyers please check here.
Nevada Petit Larceny versus other Theft Crimes
As stated previously, petit larceny is the taking of another’s personal property that is valued under $650. However, the circumstances of the crime also determine if a different type of theft is charged.
- Burglary: a noted above, burglary is entering a property with the intent to steal. A charge of burglary may apply even if the door was open. It is important to note that burglary may be charged even if no theft occurred.
- Robbery: the taking of personal property by force or threat. For example, swiping a purse from a grocery cart is simple theft, but violently snatching it away or using threats to have a person hand it over is robbery.
- Bait-purse theft: Nevada police routinely plant purses or wallets in casinos as “bait” for thieves. Taking such an item, and not attempting to locate the owner can be cause for a charge of the Nevada crime of possession of lost property.
- Possession of lost property: A charge of possession of lost property applies when a person comes into control of lost, mislaid or misdelivered property of another person under circumstances and fails to make reasonable efforts to notify the true owner.
- Possession of stolen property: It is a crime to knowingly receive or possess stolen property even if you are not the person who stole the property.
- Embezzlement: This type of crime occurs when someone steals property that was initially in their possession legally. For example, if a cashier takes a customer’s payment (legal possession), but then pockets the money instead of putting it in the register. Although embezzlement is common in the workplace, other situations occur. For example, not returning a rental car on time, or taking payment but not performing the contracted work are both considered embezzlement.
ABC Drive Safe offers one of the cheapest and easiest courses on Nevada petit larceny. It can be taken 100% online, from the location and at the time of your choosing. To find out more about this course, please click here. To buy the course please click here.